
-
Home
-
Products
-
PVC Cable Material
-
Low Smoke Zero Halogen Cable Material
-
Cable material
-
Optical fiber cable
-
-
About Us
-
VR
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

Galvanized Steel Wire has become an essential material in both construction and manufacturing applications due to its unique properties and advantages. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global galvanized steel market is projected to reach USD 200 billion by 2025, highlighting the increasing demand for durable materials in various industries. The process of galvanization, which involves coating steel with a layer of zinc, significantly enhances the wire's resistance to corrosion, thereby extending its lifespan and reducing maintenance costs. This durability is particularly advantageous in construction, where exposure to harsh environmental conditions can compromise materials.
Furthermore, galvanized steel wire demonstrates impressive strength-to-weight ratios, making it a preferred choice for a variety of applications, from reinforcing concrete to manufacturing wire mesh and fencing. A study conducted by the American Iron and Steel Institute indicates that the use of galvanized steel can lead to lower overall project costs, as projects can benefit from both reduced material wastage and increased efficiency in installation processes. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability and longevity in material choices, the role of Galvanized Steel Wire in enhancing the structural integrity and durability of projects cannot be overstated.
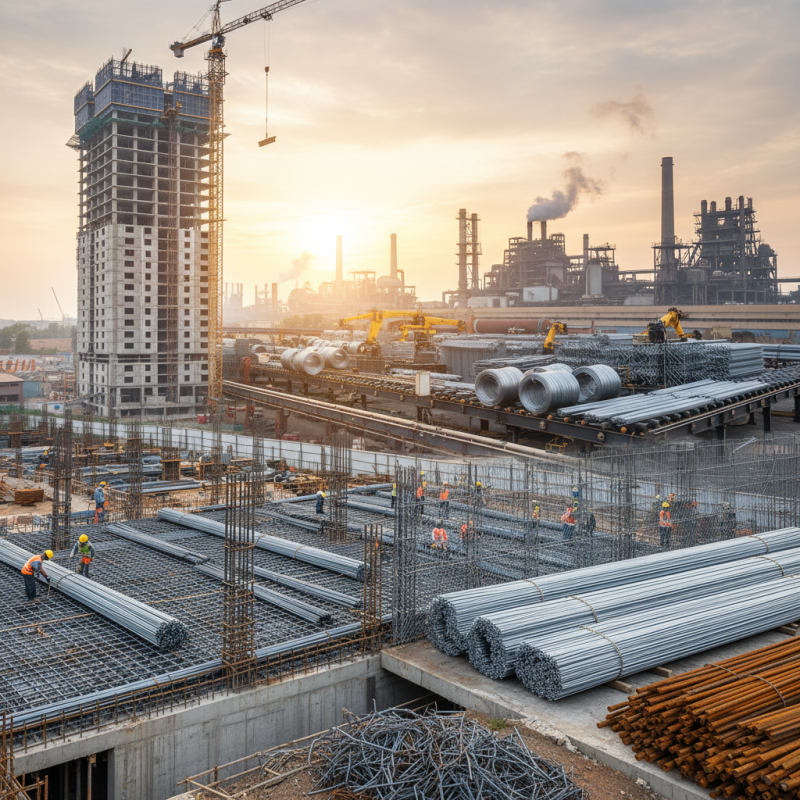

Galvanized steel wire has gained popularity in construction and manufacturing due to its exceptional properties. One of the primary advantages is its corrosion resistance, which is achieved through a process of galvanization that coats the steel wire with a layer of zinc. According to a report by the American Galvanizers Association, galvanized steel can last over 50 years in most environments, making it an ideal choice for long-term applications. This exceptional durability reduces the need for frequent replacements and maintenance, which can significantly lower operational costs.
In addition to corrosion resistance, galvanized steel wire exhibits remarkable tensile strength. This property is critical in construction applications where wires are often subjected to high loads and stresses. Studies indicate that galvanized steel wire can achieve tensile strengths exceeding 1,200 MPa, depending on the wire's diameter and the specific galvanization process employed. The combination of strength and flexibility allows for the wire to be used in various manufacturing processes, including fencing, mesh production, and reinforcement.
Tips: When selecting galvanized steel wire for your projects, consider the environment it will be exposed to, as this can influence the lifespan of the wire. Additionally, ensure that the wire's specifications align with your project requirements to maximize performance and safety. Regular inspections can also help identify wear and tear, ensuring the longevity of your construction or manufacturing applications.
Galvanized steel wire is increasingly being recognized for its superior performance across various construction and manufacturing applications. One of the primary advantages of using galvanized steel wire in these sectors is its exceptional resistance to corrosion. According to a report by the American Galvanizers Association, galvanized steel can last over 50 years in harsh environments, significantly reducing maintenance costs over time. This longevity is particularly valuable in construction, where the integrity of structural elements is paramount.
In addition to corrosion resistance, galvanized steel wire offers enhanced strength and durability. It can withstand substantial tensile load without compromising structural integrity, making it ideal for applications ranging from rebar supports in concrete structures to fencing and barbed wire systems. A study published in the Journal of Constructional Steel Research indicates that the performance of galvanized wire in construction applications can enhance overall project safety and longevity due to its mechanical properties.
Tips: When selecting materials for construction projects, consider the environment in which the materials will be used. For coastal or industrial areas, galvanized steel wire can be a cost-effective choice due to its resistance to rust and deterioration. Moreover, always ensure that the specifications meet industry standards to maximize safety and reliability.
Galvanized steel wire has become increasingly important in manufacturing due to its unique properties and versatility. One of the primary applications is in the production of industrial fencing and mesh, where the wire’s resistance to rust and corrosion ensures durability in outdoor environments. This makes it a preferred choice for securing perimeters in agricultural, construction, and commercial settings.
Furthermore, galvanized wire is commonly used to create various types of wire products, such as cable harnesses and supports, providing an excellent balance between strength and flexibility.
Another significant application of galvanized steel wire is in the automotive and construction industries. In automotive manufacturing, it serves as essential components that require high tensile strength and resistance to elements. Similarly, in construction, galvanized wire is utilized in reinforcing concrete structures, providing additional strength and support.
It is also employed in the assembly of scaffolding, where safety and stability are paramount. The ability to withstand extreme weather conditions while maintaining structural integrity makes galvanized steel wire an invaluable asset in these sectors, contributing to both efficiency and long-term reliability in manufacturing processes.
When evaluating the performance of galvanized steel wire in comparison to non-galvanized alternatives, it's essential to consider key factors such as corrosion resistance, durability, and maintenance needs. Galvanized steel wire, coated with a layer of zinc, offers superior protection against rust and oxidation. This feature makes it particularly advantageous in construction and manufacturing environments where exposure to moisture and harsh conditions can significantly compromise the integrity of materials. In contrast, non-galvanized steel wire is more susceptible to corrosion, leading to shorter lifespans and higher replacement costs over time.
Another critical aspect to consider is the overall strength and flexibility of both wire types. Galvanized steel wire not only maintains excellent tensile strength but also retains its flexibility, allowing for easier handling during installation. Non-galvanized options, while sometimes more economical upfront, can lead to increased maintenance and replacement issues due to their vulnerability to wear and tear. Additionally, the long-term cost-effectiveness of galvanized steel wire often outweighs the initial savings associated with non-galvanized alternatives, making it a preferred choice in demanding applications.
Galvanized steel wire has gained prominence in construction and manufacturing not only for its durability and strength but also for its environmental impact and sustainability. The galvanization process, which involves coating steel with a layer of zinc, enhances the material's resistance to corrosion and extends its lifespan. This longevity reduces the need for frequent replacements, which in turn minimizes waste and the environmental footprint associated with producing new steel. As industries shift towards more sustainable practices, the use of galvanized steel wire aligns well with green building principles and eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
Moreover, galvanized steel wire is fully recyclable, offering a further advantage in terms of sustainability. At the end of its life cycle, galvanized steel can be reclaimed and reused without losing quality, contributing to a circular economy. This recyclability diminishes the demand for raw materials and reduces energy consumption involved in the manufacturing processes, making galvanized steel wire an excellent choice for environmentally conscious projects. Additionally, its inherent resistance to rust and degradation means less harmful chemicals leach into the soil and water systems, thus promoting a healthier ecosystem. By incorporating galvanized steel wire into construction and manufacturing, industries can not only improve their operational efficiency but also support broader sustainability goals.
| Benefit | Description | Environmental Impact | Sustainability Aspect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Galvanized steel wire provides a protective zinc coating, preventing rust and corrosion. | Reduces the need for chemical rust inhibitors. | Extends the lifespan of steel products, reducing waste. |
| Durability | Designed to withstand harsh weather conditions and heavy loads. | Less frequent replacements lead to lower material consumption. | Contributes to long-term resource conservation. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lower maintenance costs due to corrosion resistance and longevity. | Minimizes production costs through reduced need for repurchasing materials. | Promotes economic sustainability through cost savings. |
| Recyclability | Galvanized steel can be recycled without losing its strength. | Supports circular economy by allowing reuse of materials. | Encourages recycling practices, reducing landfill waste. |
| Versatility | Used in various applications from construction to manufacturing. | Less diversity of materials needed leads to fewer environmental impacts. | Encourages the use of a single material for multiple purposes. |





