
-
Home
-
Products
-
PVC Cable Material
-
Low Smoke Zero Halogen Cable Material
-
Cable material
-
Optical fiber cable
-
-
About Us
-
VR
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

In the ever-evolving landscape of electrical engineering, the choice of Sheath Cable Material plays a pivotal role in ensuring optimal performance and durability of cable systems. According to a recent report by the International Wire and Cable Manufacturers Association (IWCM), the global demand for high-quality cable materials is set to increase by 7% annually, driven by advancements in technology and the ongoing expansion of infrastructure projects. As industries increasingly prioritize sustainability and longevity in their components, the selection of appropriate sheath materials becomes critical.
Industry expert Dr. Emily Tran emphasizes the importance of material selection, stating, "The right sheath cable material not only enhances the reliability of electrical systems but also significantly reduces maintenance costs over time." With a plethora of options available—ranging from PVC and PE to advanced materials like LSZH and thermoplastic elastomers—understanding the properties and applications of each type is essential for engineers and decision-makers alike. As we explore the best sheath cable material types in this discourse, we highlight how innovation in material science can lead to improved performance, safety, and environmental sustainability in cable applications.

When selecting sheath cable materials, it's essential to consider key types that offer optimal performance and durability for various applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is one of the most commonly used materials due to its excellent resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and electric insulation properties. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global demand for PVC in wire and cable applications is projected to reach approximately 16.5 billion USD by 2026, reflecting its integral role in the industry.
Another notable material is polyethylene (PE), which is widely recognized for its flexibility and moisture resistance. PE's lightweight nature and suitability for outdoor conditions make it an ideal choice for telecommunications and power cables. A study by Allied Market Research highlights that the polyethylene sheath cable market is expected to grow by 6.2% annually, driven by advancements in cable insulation technology and increasing demand in the renewable energy sector.
In addition to PVC and PE, cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) offers remarkable thermal resistance and durability, making it suitable for high-voltage applications. It is projected that the use of XLPE in cable production will increase significantly, with the global XLPE cable market predicted to grow to over 37 billion USD by 2027. This growth underscores the importance of selecting appropriate sheath materials to ensure long-lasting and efficient electrical performance in a variety of industrial and commercial contexts.
| Material Type | Characteristics | Benefits | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) | Flexible, durable, and resistant to abrasion. | Cost-effective, excellent insulation properties, and flame-resistant. | Residential wiring and general-purpose cables. |
| XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene) | High thermal stability and excellent chemical resistance. | Superior performance in high temperatures and better insulation than PVC. | Power cables in industrial and utility applications. |
| PE (Polyethylene) | Lightweight and resistant to moisture. | Good flexibility and low water absorption. | Telecommunications and underground cables. |
| TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) | Excellent abrasion and tear resistance. | Long-lasting durability and flexibility in harsh environments. | Flexible hose and industrial applications. |
| Rubber | Highly flexible and resilient, weather-resistant. | Good electrical insulation and high impact resistance. | Heavy machinery and outdoor equipment. |
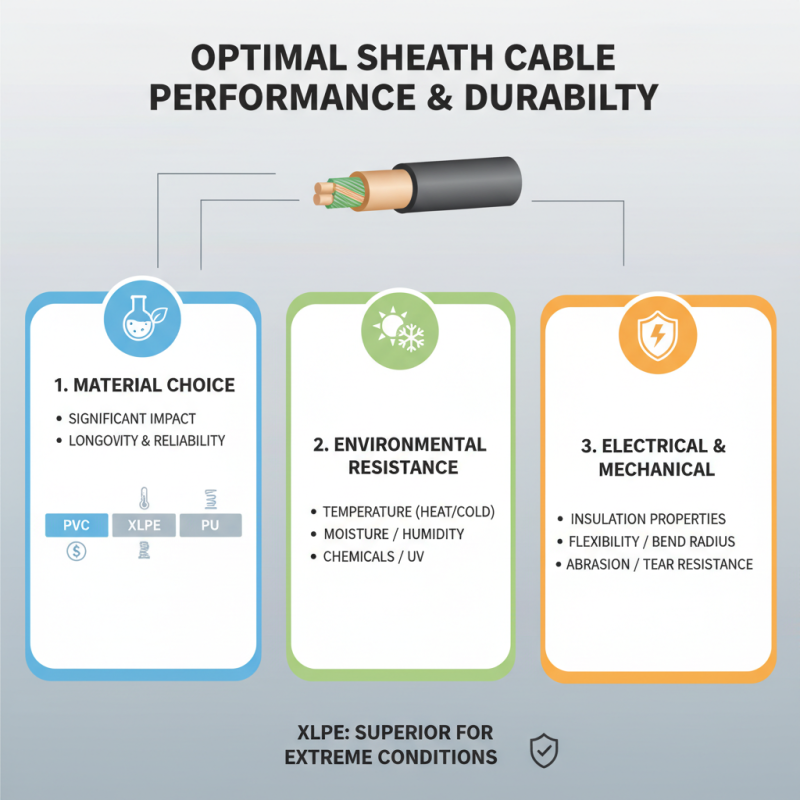
When considering the optimal performance and durability of sheath cables, several critical factors come into play. First and foremost, the choice of materials significantly impacts both the longevity and reliability of the cables. Common materials such as PVC, XLPE, and PU offer varying degrees of flexibility, resistance to environmental conditions, and thermal stability. For instance, while PVC is widely used due to its cost-effectiveness, it may not withstand extreme temperatures as effectively as XLPE, which is known for its high thermal resistance and superior electrical insulation properties.
Another essential factor influencing sheath cable performance is the environment in which they are installed. Cables used in outdoor settings must have added UV protection and be resistant to moisture, while those in industrial settings should be resistant to chemicals and abrasions. The correct selection based on the installation environment can significantly enhance the lifespan and performance of the cables.
**Tips:** When selecting sheath cables, always consider the specific environmental conditions they will encounter. Conduct thorough research on material properties and consult industry guidelines to ensure you select the most appropriate type for your needs. Additionally, regular maintenance and inspections can prevent premature wear and maintain optimal performance throughout the cable's lifespan.
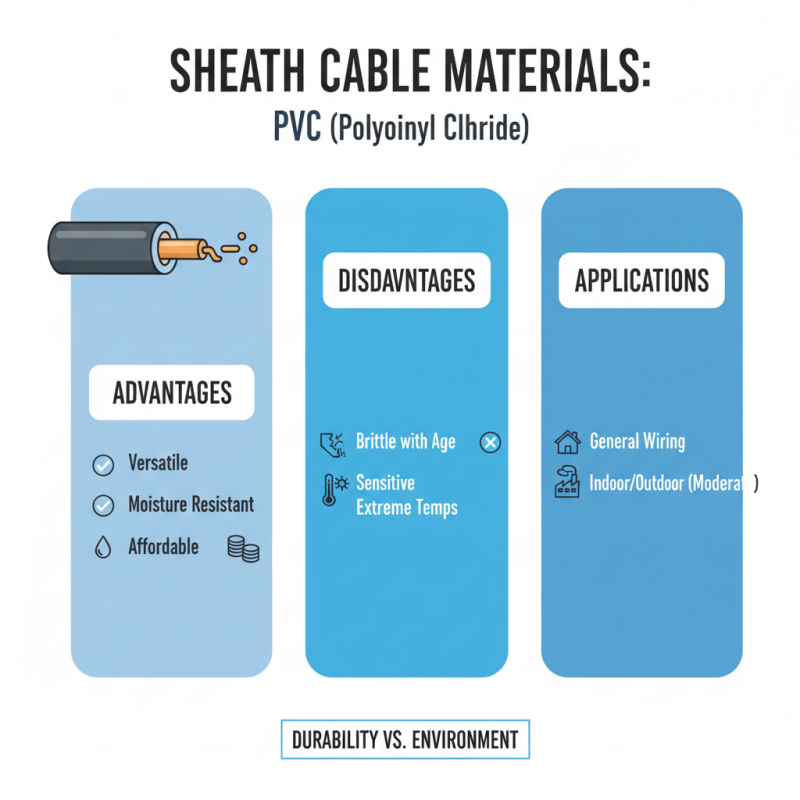
When selecting sheath cable materials, it's essential to evaluate the performance characteristics and durability of the most common options available. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is one of the most widely used materials due to its versatility, resistance to moisture, and affordability. It provides adequate protection against environmental factors and is suitable for a variety of applications. However, PVC can become brittle over time when exposed to extreme temperatures, which may affect its longevity in harsher conditions.
Another popular material is thermoplastic elastomer (TPE), known for its flexibility and resilience. TPE offers superior abrasion resistance and can withstand a broader temperature range than PVC. Furthermore, TPE is less prone to cracking, making it an excellent choice for applications in dynamic environments where cables may be subject to frequent movement. Another noteworthy material is polyethylene (PE), which is particularly effective in outdoor settings due to its excellent moisture resistance and UV stability, further extending its lifespan when exposed to sunlight.
In comparison, silicone rubber is valued for its extreme temperature tolerance and resistance to chemicals, making it ideal for specialized applications. While it generally has a higher cost, its exceptional durability in demanding environments justifies the investment. Ultimately, the choice of sheath cable material should be dictated by the specific requirements of the application, considering factors such as environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and temperature variations to ensure optimal performance and durability.
When selecting sheath cable materials, it's crucial to consider their application suitability to ensure optimal performance and durability. For environments prone to moisture or chemical exposure, materials such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) offer excellent resistance.
PVC is widely used due to its affordability and robustness, making it suitable for residential wiring and indoor applications. TPE, on the other hand, provides flexibility and resilience, making it ideal for outdoor settings or applications where cables may be subject to frequent movement.
Another important material is low-density polyethylene (LDPE), which is particularly favored for its excellent insulation properties and resistance to UV radiation. This makes it a popular choice for outdoor cables, including those used in telecommunications. For applications requiring extreme temperature tolerance, such as industrial environments, fluorinated polymers such as Teflon are recommended due to their ability to withstand high heat without degrading. Understanding these material characteristics and their suitability for specific environments is key in selecting the right sheath cable for reliable performance and longevity.
Choosing the right sheath cable material is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity in various applications. Different environments and conditions require specific materials that can withstand temperature fluctuations, humidity, and mechanical stress. Common materials include polyethylene, PVC, and thermoplastic elastomers, each offering unique properties suited for different operational needs. For longevity, it's important to consider the environment where the cables will be installed; for instance, outdoor installations might necessitate UV-resistant sheathing to prevent deterioration from sunlight exposure.
When selecting sheath cable materials, prioritize flexibility, resistance to environmental factors, and overall durability. Conduct thorough assessments of the installation site to identify potential risks such as chemical exposure or extreme temperatures. Tips: Always check for the temperature rating of the material and opt for cables that exceed the maximum expected temperature of your application. Additionally, consider using layered sheaths for enhanced protection against abrasion and chemical exposure, especially in industrial settings.
Another important factor is the clarity of specifications provided by manufacturers. Ensure that the chosen materials meet industry standards and are suited for their intended purpose. Tips: Always request samples and review material certifications to confirm compliance with safety and performance standards. This proactive approach will help you avoid costly downtimes and replacements, ensuring your cables perform reliably over their intended lifespan.





