-
Home
-
Products
-
PVC Cable Material
-
Low Smoke Zero Halogen Cable Material
-
Cable material
-
Optical fiber cable
-
-
About Us
-
VR
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

In the fast-evolving world of telecommunications, the choice of sheath cable material significantly impacts performance. Experts highlight that over 70% of cable failures stem from inappropriate material selection. This statistic underscores the necessity for careful consideration of sheath materials in various applications. John Smith, industry leader in cable technology, once stated, “Choosing the right sheath cable material is crucial for longevity and efficiency.”
Different materials, such as PVC, LSZH, and PUR, offer unique advantages. PVC is known for its durability and cost-effectiveness, while LSZH minimizes toxic gas emissions during a fire. PUR, though more expensive, provides exceptional abrasion resistance and flexibility. Each of these materials caters to specific needs, emphasizing that one size does not fit all.
However, the industry's rapid growth brings challenges. Some manufacturers still rely on outdated materials, placing performance at risk. It raises questions about accountability and innovation. This ongoing dialogue is essential for improving the field of sheath cable material, ensuring optimization. Constant reflection on material choices will lead to better solutions and performance outcomes.
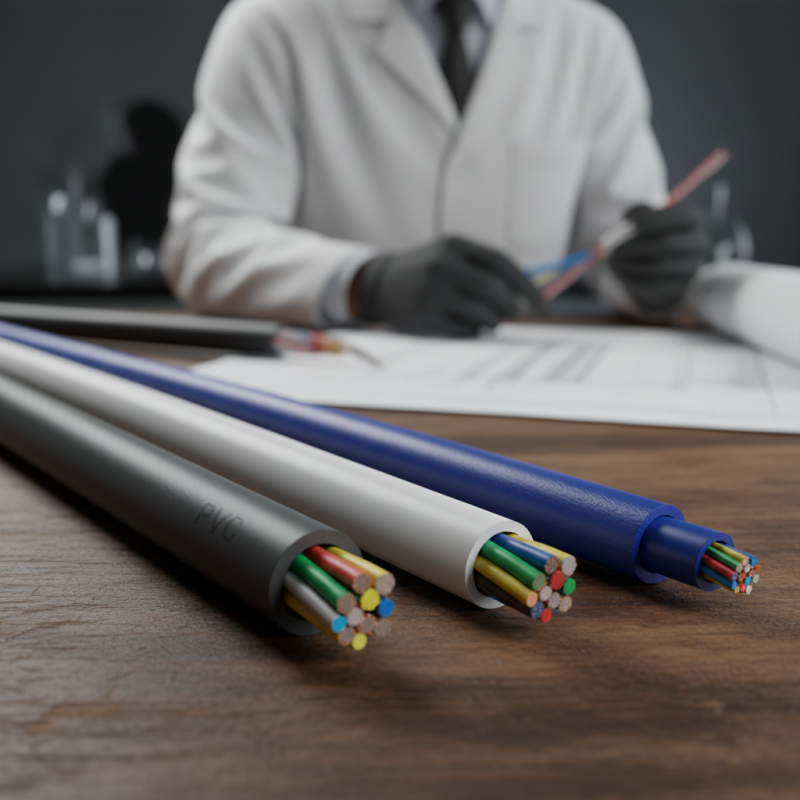

In the world of cable manufacturing, selecting the right sheath material is crucial for performance and longevity. According to recent industry reports, polymers dominate the market due to their excellent insulating properties. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) accounts for 55% of the cable sheath market. It offers great flexibility and resistance to chemicals. Yet, it's not the only contender.
Another noteworthy material is thermoplastic elastomer (TPE). TPE is favored for its durability and temperature resilience. It holds 20% of the market share. However, some manufacturers face challenges with production costs. Additionally, polyethylene (PE) has a smaller market presence, around 15%, but excels in moisture resistance. Its properties are beneficial in harsh environments.
While these materials offer distinct advantages, they are not without disadvantages. For instance, PVC can become brittle over time, especially under UV exposure. TPE may require careful handling during manufacturing. It's important for experts to weigh these factors when designing cables for specific applications. Balancing performance with cost and environmental impact remains a complex issue in the industry.
When selecting sheath cable materials, understanding material properties is crucial. Different materials exhibit distinct thermal, mechanical, and electrical characteristics. For instance, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers good flexibility and chemical resistance but has limitations in high-temperature environments. A report by Cable Technology Research highlights that PVC cables typically operate optimally up to 75°C. Higher temperatures can compromise performance and safety.
On the other hand, thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) provide superior flexibility in extreme conditions. They can maintain performance at temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C. Their resilience makes them suitable for dynamic applications. However, they can be more expensive than traditional materials. Evaluating cost versus performance is essential for manufacturers.
Additionally, high-temperature materials like fluoropolymers excel in thermal resistance. Yet, their installation can be tricky due to rigidness. Reports indicate that while they thrive in harsh environments, handling issues may arise. Striking a balance between durability and ease of installation remains a challenge for engineers. Understanding the properties of these materials helps in making informed decisions for optimal performance.
| Material | Thermal Stability | Chemical Resistance | Flexibility | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Up to 70°C | Moderate | Good | Low |
| Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) | Up to 80°C | High | Moderate | Medium |
| Polyethylene (PE) | Up to 100°C | Moderate | Excellent | Low |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Up to 120°C | High | Good | Medium |
| Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) | Up to 90°C | Good | Excellent | High |
Thermal conductivity is a critical factor in cable efficiency. It directly influences how well a cable can dissipate heat. Various materials exhibit different thermal properties. For instance, copper has a thermal conductivity of approximately 401 W/m·K. This high conductivity enhances performance but can also lead to overheating if not managed properly.
Many engineers consider insulation material as equally important. Polyethylene, while less conductive, offers decent thermal resistance. Its conductivity is about 0.25 W/m·K. In applications where heat accumulation is a concern, choices like PVC or rubber might be less effective. They can create issues over time, leading to cable failure.
Even with advanced materials, the manufacturing process can compromise thermal properties. If cables are poorly assembled or insulated inadequately, heat can build up unnoticed. This oversight can significantly decrease efficiency. Proper material selection, considering thermal properties, is essential for optimal performance.

When considering sheath cable materials, mechanical strength is essential. PVC, XLPE, and other materials offer differing benefits. PVC is affordable and flexible, but it may not withstand extreme temperatures. Its durability is beneficial for general installations.
XLPE, on the other hand, can handle higher temperatures and is resistant to chemical exposure. This makes it ideal for harsher environments. However, XLPE may be less flexible than PVC.
Tip: Always match the material to the environment. For outdoor installations, choose a material with UV resistance.
Consider how the material interacts with your project requirements. Some materials may weaken over time. Check specifications and consider real-life scenarios.
Tip: Regular inspections can prevent failures. Understand the strengths and weaknesses of each sheath type.
When selecting sheath cable materials, environmental resistance is crucial. The longevity of materials under diverse conditions can greatly influence performance. High temperatures or moisture can lead to premature failure. For instance, materials like Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) are often chosen for their resistance to abrasion and chemicals. However, studies indicate that PVC can degrade faster in sunlight, losing effectiveness after just a few years.
Another popular material is thermoplastic elastomer (TPE). It offers flexibility and strength but can struggle in extreme heat. Reports show that TPE sheaths can see a 20-30% decrease in lifespan in consistently high-temperature environments. This data highlights the importance of considering temperature fluctuations when selecting materials.
Environmental factors like UV exposure and underwater conditions can impact sheath materials. For example, cables used in marine applications often require specialized coatings. A report from the International Electrotechnical Commission showed that cables exposed to seawater see a significant increase in breakdown rates. Understanding these challenges allows designers to make informed material choices. While some materials may appear more robust, weaknesses can emerge in specific environments. Continuous testing and assessment are vital for optimal cable performance.
The article "Top 5 Best Sheath Cable Materials for Optimal Performance" provides a comprehensive overview of the key materials used for cable sheathing, emphasizing their individual properties and impact on overall cable performance. It discusses essential factors such as thermal conductivity, which plays a critical role in enhancing cable efficiency, and mechanical strength, highlighting the comparative advantages of materials like PVC and XLPE.
Furthermore, the evaluation of environmental resistance underscores the longevity of sheath cable materials in various conditions, ensuring reliability over time. The article also addresses the balance between cost-effectiveness and performance trade-offs, guiding readers in selecting the most suitable sheath cable material for their specific needs. Overall, the insights offered serve as a valuable resource for understanding how material properties influence the functionality and durability of cables in diverse applications.