
-
Home
-
Products
-
PVC Cable Material
-
Low Smoke Zero Halogen Cable Material
-
Cable material
-
Optical fiber cable
-
-
About Us
-
VR
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

In the rapidly evolving telecommunications industry, the selection of the right Optical Fiber Filling Gel is critical for ensuring optimal performance and durability of fiber optic cables. As the demand for high-speed internet continues to surge—projected to reach over 5 billion global users by 2025 according to the International Telecommunication Union—it becomes imperative for manufacturers and service providers to make informed choices regarding the materials that protect and facilitate their optical systems.
Dr. Linda Wang, a leading expert in optical materials, states, "The right Optical Fiber Filling Gel not only enhances the physical properties of fiber cables but also directly influences signal integrity and longevity." With various formulations available, each designed to cater to specific environmental conditions and operational requirements, understanding their properties can drastically impact the efficiency of data transmission and overall network reliability.
As we navigate the complexities of this essential component, a comprehensive guide to selecting the appropriate Optical Fiber Filling Gel will empower stakeholders in the industry to optimize their infrastructure, ensuring that they are equipped to meet the growing demands of today's digital landscape.

Optical fiber filling gel plays a crucial role in the performance and longevity of fiber optic cables. Its primary function is to provide protection against environmental factors such as moisture, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical stress, which can significantly impact signal integrity. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global optical fiber cable market is projected to reach $12.5 billion by 2025. As this market grows, so does the need for reliable filling gels that can ensure the optimal functioning of these cables, making this selection an essential aspect of fiber optic technology.
Choosing the right optical fiber filling gel requires a deep understanding of its thermal and physical properties. A study published in the Journal of Optical Communications highlighted that gels with low thermal conductivity can enhance the thermal stability of optical fibers, leading to better performance in varying climatic conditions. Additionally, the viscosity of the gel affects its application process; a gel that is too viscous can complicate cable assembly, while one that is too fluid may not provide adequate sealing. As the industry evolves, incorporating gels that can resist aging and UV exposure will become increasingly vital, further emphasizing the importance of selecting the right product for specific environmental applications.
This bar chart illustrates the key properties of different optical fiber filling gels based on their viscosity and refractive index, which are crucial for optimizing fiber performance.
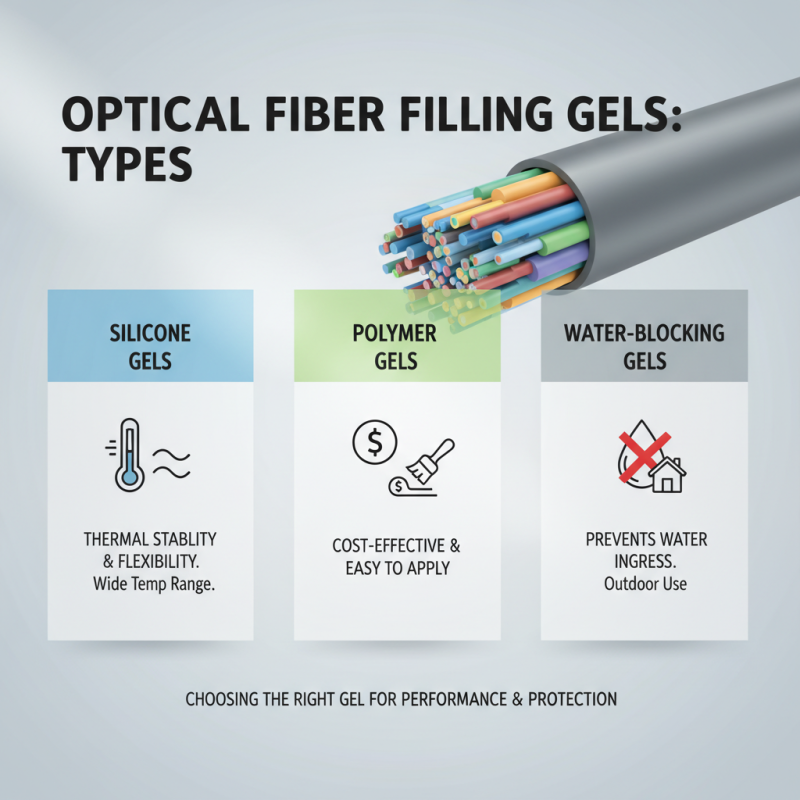
When it comes to choosing the right optical fiber filling gel, understanding the different types available in the market is crucial for making an informed decision. Optical fiber filling gels are primarily used to provide moisture protection and improve the fiber's performance, and they come in various formulations. Common types include silicone-based gels, polymer gels, and water-blocking gels. Silicone gels offer excellent thermal stability and flexibility, making them suitable for a range of temperature variations. Polymer gels, on the other hand, are often favored for their cost-effectiveness and ease of application, while water-blocking gels are specifically designed to prevent water ingress, making them ideal for outdoor installations.
Tips: When selecting a filling gel, consider your specific environmental conditions. Ensure that the gel you choose can withstand the temperature range and moisture levels typical of your installation site. Additionally, evaluating the gel’s compatibility with the optical fibers used in your application will help ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Another important factor to consider is the index of refraction of the filling gel. Gels with a matching index of refraction to the optical fibers can significantly reduce signal loss and improve overall transmission efficiency. To further optimize your choice, it may be beneficial to consult with industry experts or refer to technical specifications provided by manufacturers to ensure that you're aligning with the latest standards and technological advances.
When selecting the right optical fiber filling gel for your needs, several key factors should be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your fiber optic cables. First and foremost, evaluate the thermal stability of the gel. This characteristic is critical as it impacts the gel's ability to maintain its properties and protect the fibers over a range of temperatures. Gels that can resist degradation under high temperatures or fluctuating conditions are essential for applications in harsh environments.
Another important factor is the viscosity of the filling gel. A gel that is too viscous may not adequately fill the fiber optic tubes, leading to air pockets that can compromise signal quality. Conversely, a gel that is too thin may not provide sufficient protection against moisture ingress. It’s essential to find a balance that allows for proper coverage and sealing while maintaining ease of handling during installation. Additionally, consider the gel's refractive index, as this can affect the performance and attenuation of the fiber optics, ensuring that the signal integrity is preserved over long distances.
Optical fiber filling gel plays a critical role in the performance and durability of optical fiber cables across various industries. In telecommunications, for instance, this gel is essential for protecting the delicate fibers from moisture and mechanical stress. By filling the gaps within the cable structure, the gel ensures that the fibers remain stable and secure, which is paramount for maintaining high-speed data transmission. Its ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions makes it a preferred choice for outdoor installations, where temperature fluctuations and humidity can compromise signal integrity.
In the medical field, optical fiber filling gel is utilized in various devices that require precise and reliable light transmission. Endoscopic tools, for example, rely on fiber optics to provide illumination and visualization during minimally invasive procedures. The filling gel not only enhances the performance of these fibers but also contributes to the overall safety and effectiveness of medical interventions. Additionally, industrial applications, such as manufacturing and automation, benefit from the gel's insulating properties, which help prevent signal loss and interference in complex production systems. By understanding the diverse applications of optical fiber filling gel, industries can better select the right formulation to meet their specific needs.
| Application Industry | Recommended Gel Type | Temperature Resistance | Viscosity | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications | Low-Viscosity Silicone Gel | -40°C to 85°C | 1000 cP | Excellent moisture resistance and flexibility |
| Automotive | Polymer-Based Gel | -30°C to 120°C | 2000 cP | High thermal stability and vibration resistance |
| Aerospace | Aerospace Grade Gel | -50°C to 150°C | 3000 cP | Low volatility with superior bonding characteristics |
| Construction | Thixotropic Gel | -20°C to 70°C | 1500 cP | Easy application and excellent adhesion properties |
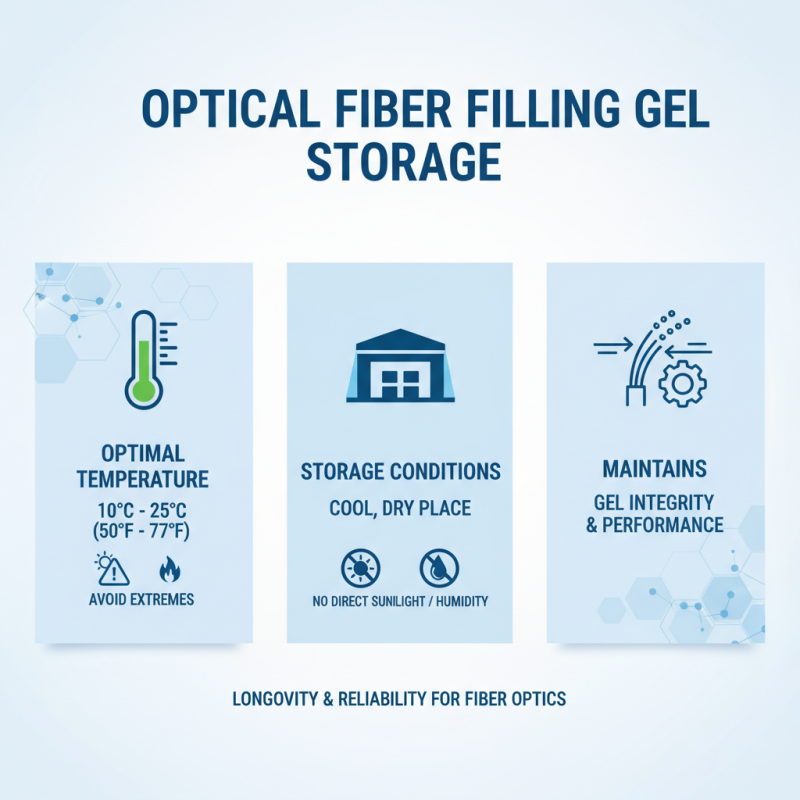
When dealing with optical fiber filling gels, proper usage and storage are critical to ensuring longevity and performance. Industry reports indicate that an optimal temperature range of 10°C to 25°C is essential for storing filling gels. Storing them outside this range can lead to chemical degradation, diminishing their effectiveness in fiber optic applications. To maintain the integrity of the gel, it should be kept in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and high humidity.
Tips: Always check the gel's expiration date before use, as expired gels may not provide adequate protection against moisture and can hinder performance. Utilize airtight containers during storage to prevent contamination and absorb moisture, which can significantly affect the gel’s properties.
Furthermore, it’s crucial to apply the gel correctly to achieve the desired optical properties. Reports highlight that improper application techniques can introduce air bubbles, which can scatter light and compromise the overall transmission quality. Ensuring a clean, dust-free environment while applying the gel can mitigate this issue. Remember to follow the manufacturer's guidelines for curing times to maximize the gel’s adhesion and functionality.
Tips: Use a clean applicator tool to apply the gel evenly, ensuring that no contaminants interfere with its performance. Additionally, after application, monitor the environmental conditions for a few hours to allow the gel to set properly.





