
-
Home
-
Products
-
PVC Cable Material
-
Low Smoke Zero Halogen Cable Material
-
Cable material
-
Optical fiber cable
-
-
About Us
-
VR
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

Phosphating Steel Wire has emerged as a critical process in various industrial sectors. This treatment significantly enhances corrosion resistance and improves adhesion for coatings. According to a recent industry report, steel wire products treated with phosphating exhibit a lifespan increase of up to 40%. This is particularly important for applications in automotive and construction industries.
In addition to corrosion protection, phosphating also enhances the surface smoothness of steel wire. A smoother surface leads to increased wire drawability, reducing production costs. Industry surveys indicate that over 70% of manufacturers prefer phosphated wire due to these benefits. However, not all phosphating processes meet the same quality standards.
Some manufacturers face challenges in achieving uniform coating thickness, which can impact performance. The technique requires careful monitoring and adjustments. While phosphating is generally effective, it is essential to recognize potential limitations. Imperfections in the process may reduce its intended benefits. Thus, understanding both the advantages and drawbacks is crucial for all stakeholders.

Phosphating steel wire significantly enhances its corrosion resistance. This process involves coating the steel with phosphate crystals, creating a protective layer. According to industry studies, phosphated steel can resist corrosion for more than 1500 hours in salt spray tests. This is a crucial factor for industries dealing with harsh environments.
One major advantage of phosphating is its ability to improve adhesion for paints and coatings. This creates a more robust barrier against moisture and corrosive elements. A report from the American Welding Society indicates that components treated with phosphating have a 30% longer lifespan compared to untreated counterparts. However, the initial setup for phosphating can be costly and requires space. This might deter some smaller manufacturers from adopting the process.
While phosphating provides excellent corrosion resistance, it is not foolproof. Certain environmental factors can still cause deterioration over time. Data shows that improper application may reduce the effectiveness of the coating. Therefore, ensuring proper procedure and maintenance is essential. Many companies struggle with consistency in their phosphating processes, leading to mixed results in corrosion resistance. This highlights the need for continuous training and quality control measures.
Phosphated steel wire plays a crucial role in industrial applications, especially due to its enhanced lubrication properties. This surface treatment creates a fine layer of phosphates, which provides a solid foundation for effective lubrication. As a result, the friction between wires or between wires and machinery significantly decreases. This leads to improved performance in processes like drawing or forming wires.
The lubrication benefits are vital for various industrial applications. For instance, in wire drawing, the phosphated surface ensures smoother movement through dies. It helps maintain the integrity of the wire's surface, reducing wear and tear. Moreover, this treatment can also minimize heat generation, which could lead to material failure. However, the long-term effects of phosphating on wire fatigue performance still need further study.
Additionally, phosphated wire may require specific lubricants for optimal performance. Choosing the wrong lubricant can counteract the enhancements provided by phosphating. Manufacturers must invest time in testing different combinations to find the best outcome. It raises questions about balancing treatment processes and lubricant selection for each unique application.
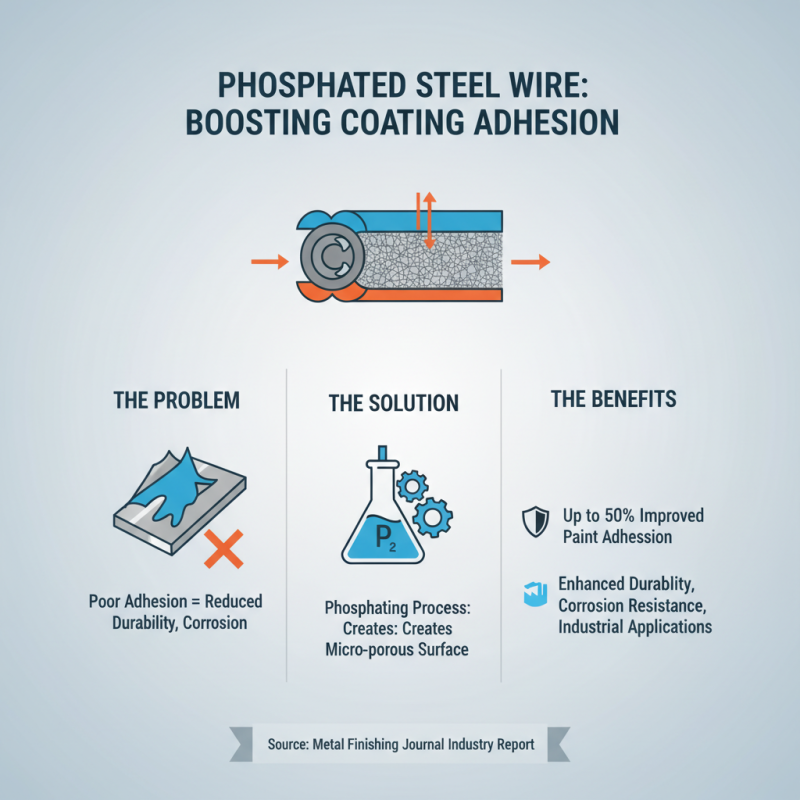
Phosphating steel wire significantly enhances the adhesion of coatings and paints. An industry report from *Metal Finishing Journal* noted that phosphated surfaces improve paint adhesion by up to 50%. This is crucial for various industrial applications where durability is key.
The phosphating process creates a micro-crystalline structure on the steel surface. This structure increases surface area, allowing coatings to grip better. Studies show that coatings on phosphated wires show a 30% reduction in peeling compared to untreated wires. Such improvements in adhesion can enhance the lifespan of products, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
However, not every application benefits equally. Surface cleanliness plays a vital role in effectiveness. If the steel wire is contaminated, the benefits of phosphating may be lost. It's essential to understand that the process requires careful control of conditions. Inconsistent phosphating can lead to uneven adhesion. This highlights the need for a thorough examination of each batch before proceeding.
Phosphating is an effective process for steel wire in industrial applications. Cost efficiency is a significant advantage. Reports indicate that phosphating can reduce rust and corrosion significantly. For industries reliant on steel wire, this means lower maintenance costs. A study found that implementing phosphating decreased corrosion rates by up to 80%.
Additionally, phosphating improves adhesion for paints and coatings. This enhancement can lead to longer-lasting finishes, which cuts down on reapplication costs. The overall savings can exceed 15% when compared to untreated wire. However, the initial investment in phosphating equipment can be daunting for some companies. The long-term savings often outweigh these initial costs, but not everyone sees it that way.
Moreover, not all phosphating processes yield the same results. Companies must evaluate their specific needs and environments. Improper application can lead to inconsistent results. While phosphating offers clear benefits, each operation must consider its unique circumstances. It’s essential to seek expert advice to optimize this process for cost efficiency.
Phosphating steel wire is a critical process in various industrial applications. This treatment enhances the wire's corrosion resistance and increases its lifespan. Studies indicate that phosphated surfaces can last up to 50% longer than untreated wires. Additionally, the phosphating process improves adhesion for coatings, making it easier to apply paints or polymers. This is essential for industries requiring durable finishes.
The strength and durability of phosphated steel wire are influenced by the quality of the phosphating process. Factors such as bath temperature, immersion time, and concentration directly impact the coating's effectiveness. A well-executed phosphating process can produce a uniform thickness of 5 to 20 microns. This layer provides a robust protective barrier. However, inaccuracies in any of these parameters can lead to weak spots and decreased performance.
Tips: Always monitor temperatures closely to ensure consistency. Regularly check bath concentrations for optimal results. Testing wire samples after phosphating can identify imperfections early. Being proactive in these areas can save costs in the long run. Phosphating is not foolproof, and adjustments might be necessary based on specific steel compositions. Continual refinement of the process can lead to significant improvements in product life.





